Appearance
定位布局
基础知识
定位的基本思想很简单,它允许你定义元素框相对于其正常位置应该出现的位置,或者相对于父元素、另一个元素甚至浏览器窗口本身的位置。
轮播图是典型的定位应用

下面弹出的二维码也可以使用定位处理

定位类型
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static | 默认形为,参考文档流 |
| relative | 相对定位 |
| absolute | 绝对定位 |
| fixed | 固定定位 |
| sticky | 粘性定位 |
位置偏移
可以为部分类型的定位元素设置上、下、左、右 的位置偏移。
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| top | 距离顶边 |
| bottom | 距离下边 |
| left | 距离左部 |
| right | 距离右边 |

HTML
<style>
body {
padding: 50px;
}
article {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: solid 6px blueviolet;
margin: 20px;
}
div {
font-size: 25px;
background: #f2a67d;
padding: 10px;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
}
</style>
...
<article>
<div>banmashou.com</div>
</article>HTML
<style>
main {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background: #1abc9c;
position: relative;
}
main div {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #f1c40f;
background-clip: content-box;
border: solid 1px #333;
color: white;
font-size: 2em;
position: absolute;
left:100%;
}
</style>
<main>
<div>banmashou.com</div>
</main>相对定位
相对定位是相对于元素原来的位置控制,当元素发生位置偏移时,原位置留白。

HTML
<style>
body {
padding: 50px;
}
article {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
border: solid 10px blueviolet;
font-size: 14px;
padding: 30px;
}
article img {
width: 50px;
position: relative;
top: -20px;
}
</style>
...
<article>
<img src="bm.png" alt="">
斑马兽斑马兽斑马兽斑马兽斑马兽斑马兽斑马兽斑马兽
</article>绝对定位
绝对定义不受文档流影响,就像漂浮在页面中的精灵,绝对定位元素拥有行内块特性。
参照元素
如果父级元素设置了 relative | fixed | sticky ,绝对定位子元素将参数此父元素进行定位。

HTML
<style>
body {
padding: 50px;
}
article {
width: 400px;
height: 100px;
border: solid 6px blueviolet;
position: relative;
}
div {
font-size: 25px;
background: #f2a67d;
padding: 10px;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0px;
}
</style>
...
<article>
<div>banmashou.com</div>
</article>默认位置
如果没有为定位元素设置偏移,将受父元素的 padding 等属性影响。但使用定位一般都会设置偏移位置。

CSS
body {
padding: 50px;
}
article {
width: 400px;
height: 100px;
border: solid 6px blueviolet;
position: relative;
padding: 20px;
}
div {
background: #f2a67d;
padding: 5px;
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}设置尺寸
可以通过定位的偏移值设置元素的尺寸。
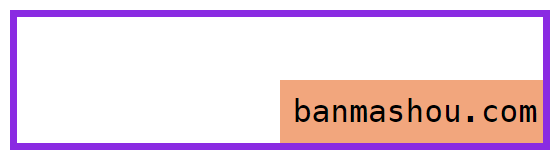
HTML
<style>
body {
padding: 50px;
}
article {
width: 400px;
height: 100px;
border: solid 6px blueviolet;
position: relative;
}
div {
font-size: 25px;
background: #f2a67d;
padding: 10px;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>居中定位
通过将 left 设置为 50% ,并向左偏移子元素宽度一半可以实现水平居中,垂直居中使用方式类似。
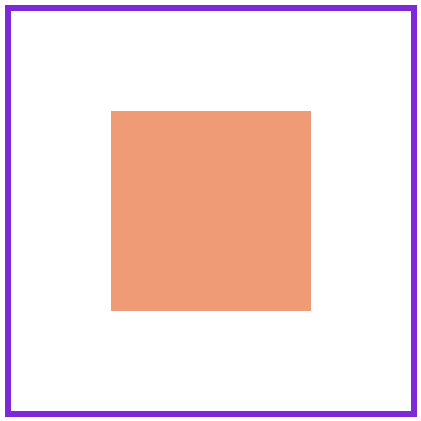
HTML
<style>
body {
padding: 50px;
}
article {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border: solid 6px blueviolet;
position: relative;
}
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: #f2a67d;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -100px;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -100px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div></div>
</article>滚动行为
固定定位元素会随滚动条发生滚动。
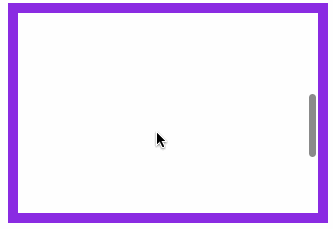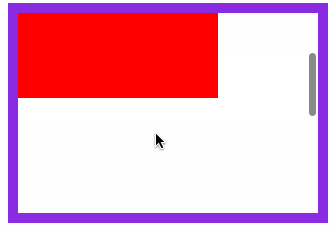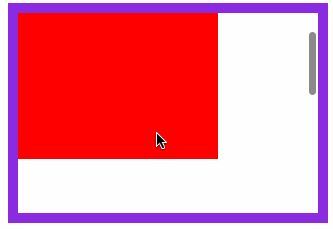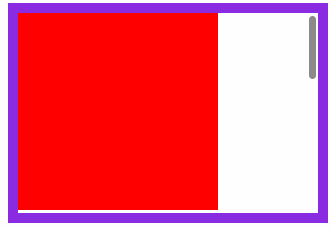
HTML
<style>
body {
padding: 50px;
}
main {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: solid 10px blueviolet;
position: relative;
overflow: scroll;
}
main article {
height: 600px;
}
main article div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
position: absolute;
}
main article div:nth-of-type(1) {
background: red;
left: 0px;
z-index: 2;
}
</style>
...
<main>
<article>
<div></div>
</article>
</main>图标定位
有了绝对定位我们可以很方便的控制元素在任何位置的摆放。

HTML
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
main {
height: 3000px;
padding: 100px;
}
main div {
width: 300px;
border: solid 6px blueviolet;
padding: 0;
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
}
main div img {
max-width: 300px;
float: left;
}
main div span {
display: inline-block;
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
line-height: 2em;
border-radius: 50%;
background: blueviolet;
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(100, 100, 100, 0.8);
}
</style>
...
<main>
<div>
<span>热</span>
<img src="banmashou.jpg" alt="">
</div>
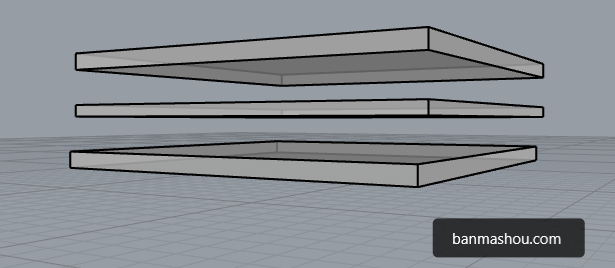
</main>纵向重叠
如果元素重叠在一起,可以使用 z-index 控制元素的上下层级,数值越大越在上面。
父级子元素设置 z-index 没有意义,子元素永远在父元素上面的。
层级改变
HTML
<style>
body {
padding: 50px;
}
article {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: solid 10px blueviolet;
position: relative;
cursor: pointer;
}
article:hover div:nth-of-type(2) {
z-index: 2;
}
article div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
position: absolute;
}
article div:nth-of-type(1) {
background: red;
left: 0px;
z-index: 2;
}
article div:nth-of-type(2) {
background: green;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
</style>
...
<article>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</article>购物车
因为事件捕获特性,所要以把父级的 z-index 放在最下面。

HTML
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
main {
width: 600px;
padding: 100px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
main article {
width: 150px;
position: relative;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 14px;
color: #555;
}
main article:hover div:nth-of-type(1) {
border-bottom: none;
}
main article:hover div:nth-of-type(2) {
display: block;
}
main article div {
box-sizing: border-box;
height: 50px;
line-height: 3.5em;
text-align: center;
border: solid 2px blueviolet;
background: white;
}
main article div:nth-of-type(1) {
position: relative;
z-index: 2;
}
main article div:nth-of-type(2) {
display: none;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
top: 48px;
left: -150px;
z-index: 1;
}
</style>
...
<main>
<article>
<div>我的购物车</div>
<div>购物车中暂无产品</div>
</article>
</main>固定定位
元素相对于页面固定定位在某个位置,固定定位元素不会在滚动时改变位置 ,使用position: fixed 产生固定定位。
HTML
<style>
header {
height: 60px;
border-bottom: solid 5px #7f35c9;
box-shadow: 0 5px 8px rgba(100, 100, 100, 0.6);
position: fixed;
top: 0px;
left: 0px;
right: 0px;
}
article {
height: 3000px;
margin-top: 80px;
background: #f3f3f3;
border: solid 5px #ddd;
}
</style>
...
<header></header>
<article></article>粘性定位
同级定位

HTML
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
main {
padding: 30px;
font-size: 14px;
}
main article {
width: 400px;
height: 100px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
overflow: scroll;
}
main article h2 {
background: #db1f77;
color: white;
text-indent: 20px;
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}
main article h2:nth-of-type(1) {
background: blueviolet;
}
main article section {
height: 300px;
}
</style>
...
<main>
<article>
<section></section>
<h2>斑马兽</h2>
<section></section>
<h2>banmashou</h2>
<section></section>
</article>
</main>非同级定位
不属于同一个父元素设置粘性定位时,后面的元素挤掉原来位置的元素。

HTML
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
main {
padding: 30px;
font-size: 14px;
}
main article {
width: 400px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
height: 200px;
overflow: scroll;
}
main article section:nth-of-type(odd) h2 {
background: blueviolet;
}
main article section h2 {
background: #db1f77;
color: white;
text-indent: 20px;
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}
main article section p {
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
...
<main>
<article>
<section>
<h2>斑马兽</h2>
<p>
banmashou.com
</p>
</section>
<section>
<h2>欣欣吖</h2>
<p>
xinxinya.com
</p>
</section>
<section>
<h2>baidu.com</h2>
<p>
百度
</p>
</section>
</article>
</main>